您所在的位置:首页 - 科普 - 正文科普
plc乘法运算梯形图
![]() 圣昂
2024-05-03
【科普】
297人已围观
圣昂
2024-05-03
【科普】
297人已围观
摘要**Title:AComprehensiveGuidetoPLCMultiplicationProgramming**Inindustrialautomation,ProgrammableLogicC
Title: A Comprehensive Guide to PLC Multiplication Programming
In industrial automation, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are widely used for controlling machinery and processes. Multiplication is a fundamental arithmetic operation in PLC programming, crucial for various applications such as scaling ***og signals, calculating motor speeds, and determining process parameters. This guide will delve into the intricacies of PLC multiplication programming, providing insights, examples, and best practices.
Understanding PLC Multiplication:
Before delving into programming, let’s grasp the basic concept of multiplication in PLCs. Multiplication involves two operands – multiplicand and multiplier – and results in their product. In PLC programming, multiplication is typically represented by mathematical instructions or function blocks.
PLC Multiplication Instructions:
Most PLC programming languages provide specific instructions for multiplication. Here’s an overview of multiplication instructions in popular PLC programming languages:
1.
Ladder Logic (LD):
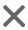
In ladder logic programming, multiplication is usually performed using math functions or instructions such as `MUL` or `MULI`.
Example:
```
LD MUL Multiplier // Multiply Operand1 by Operand2
```
2.
Structured Text (ST):
ST allows mathematical operations through arithmetic operators like `*`.
Example:
```plc
Product := Operand1 * Operand2; (* Multiply Operand1 by Operand2 *)
```
3.
Function Block Diagram (FBD):
In FBD, multiplication is achieved using function blocks like `MUL`.
Example:
```
MUL (Operand1, Operand2, Product); // Multiply Operand1 by Operand2 and store in Product
```
4.
Sequential Function Chart (SFC):
Multiplication in SFC can be achieved using various programming elements depending on the specific PLC software.
Best Practices for PLC Multiplication Programming:
1.
Input Validation:
Ensure that the input values (multiplicand and multiplier) are within acceptable ranges to avoid calculation errors and unexpected behavior.
2.
Data Types:
Pay attention to data types to prevent data overflow or loss of precision. Use appropriate data types based on the application requirements.
3.
Scaling Factors:
When dealing with ***og signals or sensor inputs, apply scaling factors before multiplication to convert raw values into meaningful engineering units.
4.
Error Handling:
Implement error handling routines to manage exceptional conditions such as division by zero or overflow situations. This enhances the robustness of the control system.
Example Application: Motor Speed Control
Let’s consider a practical example of PLC multiplication programming for motor speed control:
Problem Statement:
You need to control the speed of a motor based on the input voltage signal received from a sensor. The motor speed is directly proportional to the input voltage signal, with a scaling factor of 100.
PLC Multiplication Program (Structured Text):
```plc
PROGRAM Motor_Speed_Control
VAR
InputVoltage : REAL; (* Input voltage signal *)
ScalingFactor : REAL := 100.0; (* Scaling factor *)
MotorSpeed : REAL; (* Motor speed output *)
BEGIN
(* Read input voltage from sensor *)
InputVoltage := ReadInputVoltage();
(* Calculate motor speed *)
MotorSpeed := InputVoltage * ScalingFactor;
(* Control motor speed *)
ControlMotorSpeed(MotorSpeed);
END_PROGRAM
```
Conclusion:
Multiplication is a fundamental operation in PLC programming, extensively used in various industrial automation applications. By understanding the principles and best practices of PLC multiplication programming, engineers can develop efficient and reliable control algorithms for diverse automation tasks. Whether it’s scaling ***og signals or implementing complex control algorithms, mastering PLC multiplication programming is essential for effective PLCbased automation solutions.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip PLC programmers with the knowledge and insights necessary to tackle multiplication tasks effectively, contributing to the advancement of industrial automation systems.
Tags: plc32位乘法指令 plc乘法指令用法 plc程序编程
版权声明: 免责声明:本网站部分内容由用户自行上传,若侵犯了您的权益,请联系我们处理,谢谢!联系QQ:2760375052
上一篇: 新能源汽车行业前十
下一篇: 芦淞线下编程培训机构
最近发表
- 探索日本核污染水排放,现状、影响与应对策略
- 全职妈妈离婚获2万元经济补偿,揭秘背后的真相与启示
- 王琳惊艳亮相,54岁穿短裙婚纱走秀的优雅与活力
- 继续深耕中国,共创共享机遇
- 千位歌迷在刀郎演唱会现场外,音乐盛宴如梦如幻
- 渔船遇海盗袭击,3名中国人失踪,紧急救援与深入理解
- 小米试驾体验遇尴尬,雷军秒道歉引热议
- 香港歌手李国祥去世
- 音乐人因刀郎跨越西洋乐与中国音乐的奇妙转变——深度解读与启示
- 清华毕业生失踪背后的罗生门,揭开真相与寻找答案
- 韩国救山火消防员盒饭,一份充满人间温情的瞬间
- 黄金价格的终极目标,探寻价值与投资方向
- 小区惊魂,儿童车祸事故的警示与启示
- 湖南38个机关事业单位围墙全拆,开启新篇章
- 车主掉头遇红灯,后车滴滴巧应对
- 探索云南曲靖市会泽县的地震事件
- 新郎没拉裤子拉链,新娘手动闭链的浪漫婚礼
- 10岁女孩高烧去世,被诊断为7种疾病
- 拥抱与冒险,两个小孩的温馨瞬间与泥坑的奇妙旅程
- 女厅官落马后,下属被查风波掀起波澜
- 勇敢逆行,诠释人间大爱——关于溺亡外卖员及其家庭的故事
- 大摩小摩去年四季度疯狂买A股
- 从人去楼空歌词中读懂离别的深情与生命的哲思
- 甲亢患者学功夫之路,挑战与成长
- 九牛一毛歇后语——生活中的小智慧大道理
- 多名大陆配偶被限期离台 台各界发声
- 和巧虎一起玩躲猫猫,让孩子在游戏中学习与成长!
- 王者荣耀游戏体验优化与应对关键问题的应对策略
- 探索趣味与成长的数字乐园
- 地震的力量,缅甸与汶川地震的对比
- 畅享军事模拟游戏的无限乐趣
- 缅甸地震,灾难中的救援与应对
- 董宇辉报平安,温馨时刻
- 机战王洛洛历险记全集——一场童年的奇幻冒险之旅
- 揭开美军飞行员之怒,深入了解行为后果与安全责任
- 揭开全国重名查询系统的神秘面纱,如何轻松找到与你同名的人
- 缅甸地震中的救援行动与启示
- 揭秘你的另一个星座,探索隐藏的性格密码
- 东旭集团证券违法拟被罚17亿元
- 深入解析暗黑破坏神攻略,助你成为圣休亚瑞的传奇英雄
- 专家解读地球是否进入活跃期文章标题
- 畅玩经典——实况足球10中文版的全面解析与攻略
- 牛肉市场中的中方与美国厂商,续约与挑战
- 畅玩捕鱼达人单机版,轻松体验水下冒险的乐趣
- 王钰栋应对脚踝受伤,回应与处理
- 探索自然的灯塔——野外女教师的角色与魅力
- 华阳集团,2024年净利润增长引领行业新篇章
- 探索南美大陆的地理瑰宝
- 男子做马拉松陪跑一场收入6000元
- 69岁阿姨的退休生活,自驾游的传奇之旅文章标题及内容